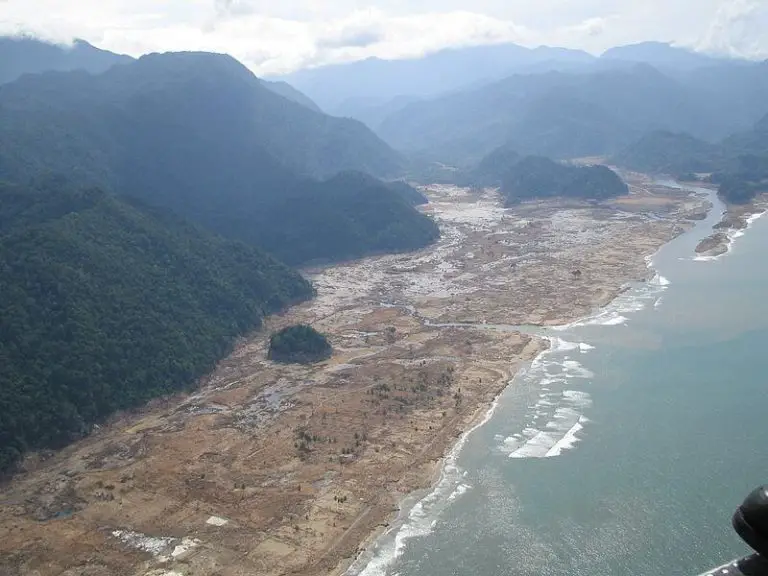

WHAT ARE TSUNAMIS ?
Tsunamis are like huge walls of water, they are the most destructive waves on the planet. They can reach up to speeds of 800 km per hour, and can reach heights of 40 meters above the normal level of the sea. The waves contain millions of tons of water.
Anything that is in a path of a big tsunami, whether it is schools, trees, homes, cars, boats or people, will be all swept away, crushed or buried under water.
Towns and villages that are most in danger from tsunamis are those at sea level, and less than 2 km from the sea. Even a small tsunami could easily travel a long distance over flat land like this.
Over the last 100 years or more, tsunamis have caused billions of pounds worth of damage, and has killed hundreds of thousands of people all around the world.

Normally in the oceans as the waves moves into the coast and into shallow water, the tips of the waves curl over and breaks. In contrast, tsunamis waves are a huge wall of fast moving water, that rarely breaks as it nears the shore.
“Tsunami” is a Japanese word for “Harbor wave.” It gets this name from all the devastation it causes around the coastal harbors of Japan.
WHAT CAUSES TSUNAMIS ?
Most tsunamis are caused by earthquakes at the bottom of the ocean, when a giant chunk of land (Tectonic Plates) drops down as the Earth’s crust suddenly moves. When this happens, millions of tons of seawater moves in to fill the gap, which causes a series of waves on the oceans surface. From this, a tsunami is born.
Tsunamis are not always caused by earthquakes, they can also be triggered when large amounts of rock or ice on mountains, suddenly break free and fall into the water.
They can also form when underwater volcanoes explode, or even if a large meteorite plunged into the ocean.
One has to understand about tsunamis, is that earthquakes and volcanoes can happen underwater, not just on land.
Tsunamis are natural events that has happened throughout the history of our planet. Just as we cannot prevent earthquakes or volcanoes, we cannot prevent tsunamis either.
WHAT ARE TECTONIC PLATES !!!
Tectonic plates, located in the Earth’s crust are composed of solid rock, while under the plates is a weaker layer of dense melted rock. It’s between these two boundaries, that the plates, which are constantly moving over the weaker layer, that the most dramatic earthquake and volcanic action happens.
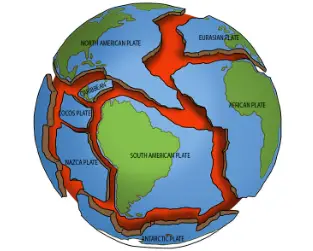
For example, if two plates are sliding past and over each other, massive friction stores energy within the plates. The plates can become stuck to each other, and it’s only when they finally pull apart, we experience an earthquake on the Earth’s surface.
Tectonic plates are massive, irregular shaped slabs of solid rock. The size of these plates vary greatly, from a few hundred, to thousands of kilometers across.
WHERE DO TSUNAMIS MOSTLY OCCUR ?
Around 9 out of 10 tsunamis happen within the Ring Of Fire, a region in the Pacific Ocean where earthquakes and volcanic eruptions frequently take place. There has been at least one tsunami a year in the Pacific Ocean since 1800, plus there will be more in the future.
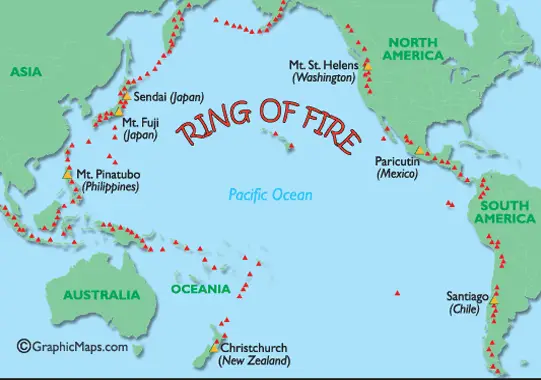
Tsunamis are most common in the Pacific Ocean, so countries such as Japan, Chile and the United States, who have long coastlines on the Pacific Ocean, are all at risk of being hit by a tsunami, but in saying this, a tsunami can happen in any major body of water, including lakes.
Most tsunamis are barely recognizable in deep parts of the oceans, but they do get bigger as they approach land.
SIGNS OF A TSUNAMI !!!
When a tsunami is about to strike the coast, first of all, the sea level drops as the water is suddenly sucked from the shoreline, uncovering the sea floor, and leaving fish and boats stranded.
This happens because all the water has relocated to fill the space on the ocean floor caused by an earthquake. Next of all, the water returns in a series of waves called a wave train. The time difference between each wave varies from minutes, to even an hour.
After each wave the water is sucked back out to sea, before it shoots back in again. The first wave normally is not the worst, the most dangerous waves has still to come.
Seemingly the third and eight wave in the wave train is the biggest and most dangerous to human life. The whole of the coastline may be altered by these walls of water.
A big tsunami can have catastrophic effects to mankind. Many people and animals may be drowned, or even carried up to a kilometer inland. The infrastructure of the town or village will not return to normal for sometime.
In a instant during a tsunami, whole areas of homes, farms and factories could be wiped out, let alone the many health hazards, such as the risk of electrocution from broken power lines, polluted water from snapped pipes, and leaking gas from broken pipes exploding. The list is endless. The cost could run into billions, but there is things money cannot buy, and that is LIFE.

The signs of a tsunami would be the rumbling in the ground from an earthquake, or if the water on the shoreline pulls back leaving bare sand. If this happens, then its time to run to higher ground. But if by chance you are caught in one, your best chance of survival is to find a floating object and hold on for dear life.
INTERESTING FACTS ON TSUNAMIS !!!!
Scientists based in Hawaii, have established the Pacific Tsunami Warning System. It’s a network of seismic-monitoring stations and sea-level gauges. They can detect earthquakes and abnormal changes in sea level. It helps the scientists to decide whether a tsunami has been triggered by an earthquake.
Scientists from the U.S and Japan have laid cables on the oceans floor, close to the coast. Connected to the cables are censor boxes that can detect when a deep tsunami wave passes over them. The boxes sends this information via satellite to scientists onshore, who then takes whatever course of action is required.
Nowadays, thanks to better communication systems, authorities use radio and TV broadcasts to warn people if there is a need to evacuate. Then the fire, police and ambulance services are put on red alert, and the hospitals prepare to treat tsunami victims. In most cases the police and the army usually help to organize the evacuations.
Anyone on boats near the coast should head out to sea if they hear a tsunami warning. Boats near the coast will be tossed and smashed onto the shores like toys.
The most deadliest tsunami recorded was on the 26th December, 2004, in the Indian Ocean. The earthquake that generated this tsunami is estimated to have released the energy of 23,000 Hiroshima-type atomic bombs. It unleashed a series of killer waves that sped across the Indian Ocean. It affected 12 different countries, leading to more than 225,000 fatalities, and millions more homeless, making it perhaps the most destructive tsunami in history.

Since 1800, over 40 tsunamis have hit Hawaiian islands. Hawaii has about one tsunami every year, and a serious one every seven years. Nowadays in Hawaii, many offices and hotel buildings are now designed on stilts. The ground floor is open parking space, so that the water will pass through the space, and not damage the building structure.
On average, two tsunamis occur per year causing damage near the source, and approximately every 15 years, a destructive tsunami occurs.
Sometimes tsunamis are called tidal waves, but this is incorrect as tidal waves are caused by the pull of gravity of the moon and the sun. High tide may sometimes cause large tidal waves, but never tsunamis.





