
INTERESTING FACTS ABOUT SPACE PROBES !!!
Since the late 1950’s, space probes have been sent up to explore the solar system.
A space probe is a unmanned robotic spacecraft that does not orbit Earth, but instead, investigates in deep space and transmits their findings back to Earth.
A space probe is about the size of a family car. They are launched from Earth by rocket or space shuttle, to travel to a certain target.
A space probe might also carry a second smaller probe for release into an atmosphere .
Some space probes might often carry a space lander craft. The craft is then released to touchdown on planetary or lunar surfaces.

To date, space probes have investigated all the solar system planets, taken a look at many of the moons, comets, asteroids, and have even studied the Sun.
Every space probe has different missions and collects different data.
Most probes are powered by a combination of batteries and solar panels.
Most probes are not designed to return to Earth. Some have landed on planets and some have just flown past the planets, taking pictures for scientists to investigate. All the information they gather is used to understand the weather and other changes that happens on planets, other than Earth.
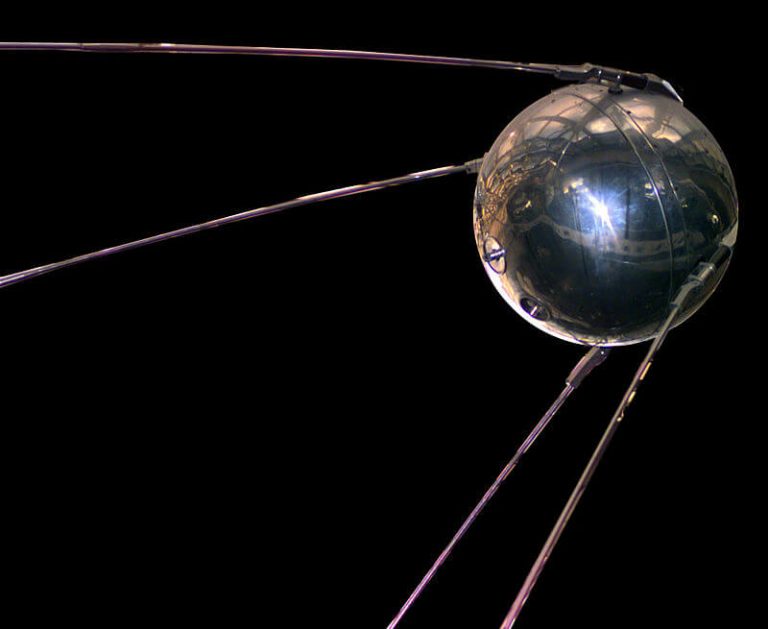
The first probe (satellite) to go up into space was the Sputnik 1. It was launched on Oct 4, 1957, by the former Soviet Union.
The Luna 1, launched by the Soviet Union in 1959, was the first man-made object to go into orbit around the Sun.
Space probes do not have astronauts.
There are three different types of space probes. There are lunar (moon) probes, solar (sun) probes, and probes that investigate the rocky surfaces on planets, or the gases on gaseous planets. They all have different missions.
The first probe to land on Mars, and transmit pictures from it’s surface back to Earth, was the Luna 9, on February 3rd, 1966.

Probes use radio waves to send information back to Earth, or sometimes to a manned spacecraft.
From 1975-82, Russia had six probes land on the surface of Venus, successfully taking photos in temperatures of 855° Fahrenheit.
The Soviet Union launched the Korabl-Sputnik 5 probe on the 19th of August, 1960, into orbit with 2 dogs, 40 mice, 2 rats, and a variety of plants. One of the dogs later had puppies, one of which was sent to the then First-Lady, Jackie Kennedy.
The Korabl-Sputnik 5 was the first spaceflight to send animals into orbit and return them back safely to Earth. It paved the way for the first human orbital flight.
The Parker Solar Probe was launched by NASA, in August of 2018. It’s mission is to get closer to the Sun than any other probe has ever been before. The probe will arrive to the closest point to the Sun by 2024, which will provide scientists with the closest view of the star.
The Parker Solar Probe is named in honor of the physicist Eugene Parker, at a cost of 1.5 billion dollars.
The Soviet Union probe, Luna 15, actually crashed into the surface of the moon, while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin were still on it.
As compared to crewed flights, automated space missions are far more economical, and of course, less risky to human life.
Billions of dollars worth of facilities, and hundreds of people are involved in following the flight of each space probe, and in intercepting the data it transmits back to Earth.
Up to 160 unmanned space probes have been launched, since the former Soviet Union first launched the first space probe, Sputnik, in 1957.
On July 19th, 2020, the United Arab Emirates launched it’s first ever unmanned spacecraft on a mission to Mars, off the southern coast of mainland Japan. The $200 million “Hope Probe” is scheduled to arrive in February 2021, when it will enter into orbit around the Red Planet and begin it’s missions, marking the first planetary science mission led by an Arab country.
The space probe HOPE, was the first of three space missions sent towards Mars during July of 2020, with missions also launched by the national space agencies of the U.S.A and China. They are all expected to arrive at Mars in February 2021.
On the 6th December, 2020, a space probe carrying samples from an asteroid called Ryugu was retrieved from the remote Australian outback after a six-year mission. The capsule from the unmanned Hayabusa2, carried the first extensive samples of dust from an asteroid. The capsule’s samples could contain clues to the origin of the solar system. The samples which may also contain information about life on our planet, was taking to a research facility owned by the Japan Exploration Agency (JAXA).
On the 9th February, 2021, the United Arab Emirates became the fifth country to ever reach Mars, with its space probe, named Hope. After a seven month flight, it successfully entered into orbit around the red planet. The $200 million satellite aims to provide a picture of the Martian atmosphere for the first time, and study daily and seasonal changes on the planet. This is hopefully the first of three space missions to reach Mars this month, with China and the U.S. also sending space probes in quick succession.
China became the sixth nation to ever reach Mars, after its Tianwen-1 probe arrived in orbit around the Red Planet on February the 10th, 2021. Following a seven-month flight, the five-ton orbiter with a lander and a solar-powered rover in tow, will attempt to land on the Martian surface in May, and spend up to three Earth months studying the planet’s soil and atmosphere.
This milestone by China, sees them join the United States, the Soviet Union, India, the European Space Agency and the United Arab Emirates, who have all successfully sent probes to Mars.
NASA’s Perseverance probe landed safely on Mars on Thursday the 18th of February, 2021, after traveling some 300 million miles in nearly seven months. Over the next two years, Percy, as it is nicknamed, will use its 7ft (2 meters) arm to drill into the local rocks, looking for evidence of past life. The six-wheeled vehicle is equipped with a record 25 cameras and two microphones. NASA has describe Percy as the most ambitious of nearly 20 U.S. missions to Mars, dating back to 1965. The total cost of the mission could hit $3 billion.
On April 19th, 2021, NASA made history when the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter successfully lifted off from the Martian surface, flew, and landed safely, opening the door for a new generation of space drones. The 4-pound (1.8kg) drone climbed about 10 feet above the ground and hovered for 30 seconds, showing that rotorcraft technology can work in that kind of harsh environment. The Perseverance rover, which carried Ingenuity to Mars, filmed the successful liftoff from a nearby overlook. Ingenuity is the first craft to achieve controlled, powered flight on a planet beyond Earth.

On May 14th, 2021, China’s probe to Mars successfully touched down on the Red Planet. The Tianwen-1 vessel touched down in an icy area of Mars known as Utopia Planitia. It had reached Mars in February and had been in orbit since. The Tianwen-1 mission consists of an orbiter, a lander and a rover called “Zhurong”, which is about the same size of a small car and comes equipped with six scientific instruments, including a high-resolution topography camera. When the rover rolls of the lander it will join the US’ Perseverance and Curiosity rovers to explore the surface of the Red Planet.





